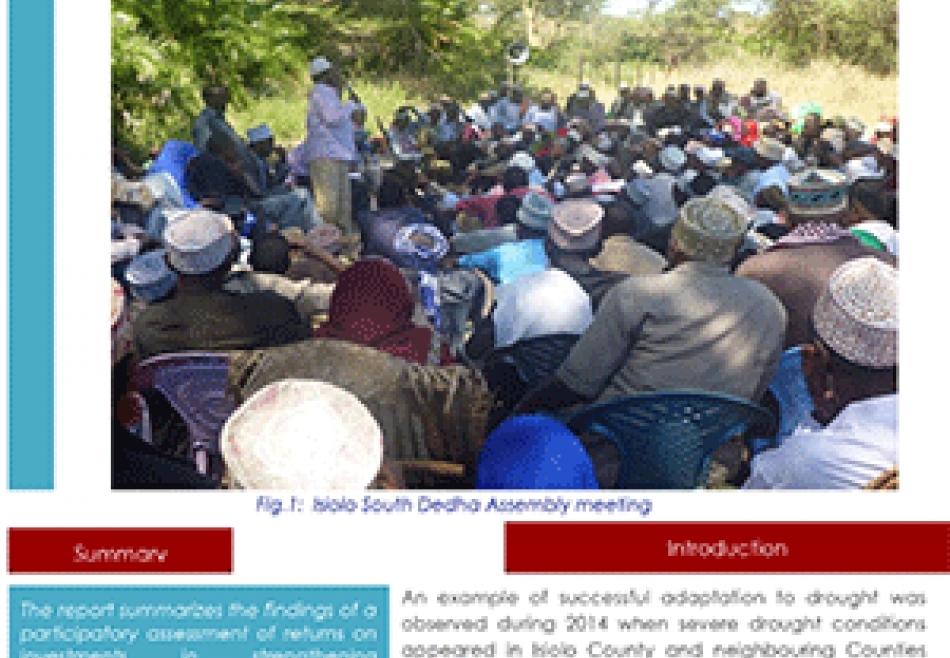
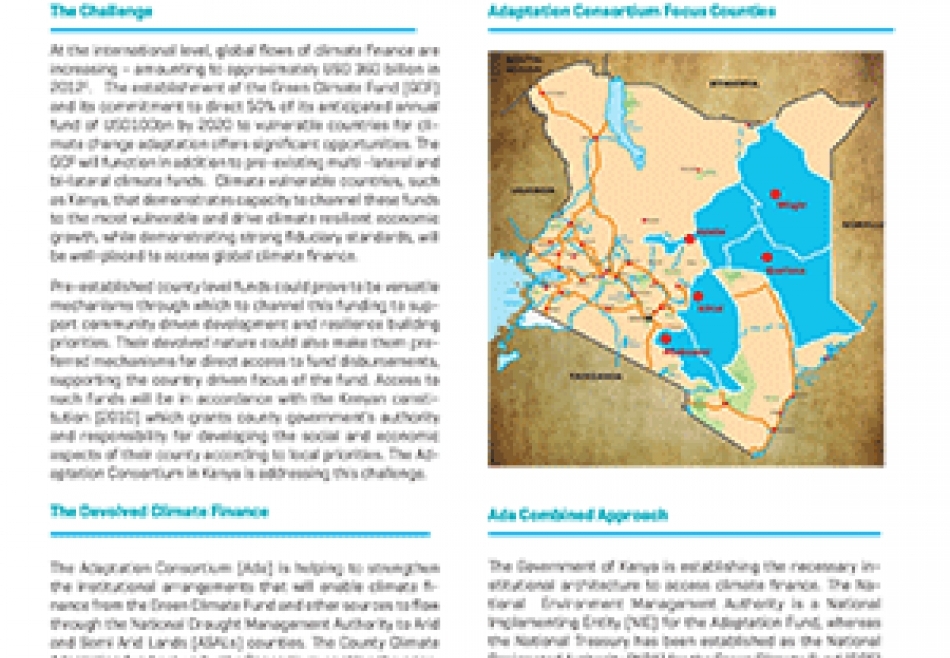
The County Climate Change Fund (CCCF) mechanism is an example of a new devolved climate fnance mechanism piloted by five county governments of Isiolo, Kitui, Makueni, Garissa and Wajir from 2013 to deliver climate finance from the national to local level. The Adaptation Consortium conducted a learning exercise to gauge the effectiveness of the CCCF Mechanism to improve climate resilience…